Encryption
I think we know why encryption is important: It’s a way to store or transmit data without allowing everyone, except those intended, to see it. I think it’s important to focus on those two similar but different concepts; in transit and at rest.
At work, as you deal with vendors or look for new applications, make sure you ask them how they store your data (at rest) and how that data is shared (in transit). Whether the data lives in the cloud or not, make sure that you are the only entity that has keys to that datastore. To everyone else, it should be encrypted, including the people hosting that storage. If the company or people you are dealing with don’t have an answer for this, walk away.
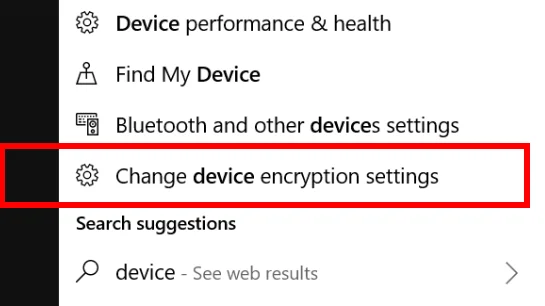
At home encryption is a little trickier, but for the majority of users, Windows 10 Home finally has encryption, provided for free.
On the Device encryption screen, make sure that your Device Encryption is on. Keep in mind, this means nothing if you don’t have a password on your device (more on that later).
If you’d like to go the extra mile, click on BitLocker settings on the right and back up your keys to a secure location. This secure location could mean a password protected removable drive, or USB stick or stored in a fire safe or a trusted location offsite.
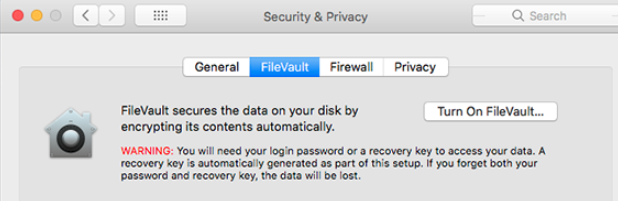
For Apple products, use FileVault to encrypt the entire drive, similarly you can back up the keys.
Once the drive is encrypted, the files on the drive are harder or near impossible to get to. This helps when your laptop is stolen, but it can cause problems in the case of a computer crash. You or Geek Squad won’t be able to simply pull the drive out and mount it from another device, you actually need to have the recovery keys to access that data, so backups of those keys are very important, otherwise that data could be lost forever. Similarly, backing up important data to a protected external drive on a regular basis is recommended.
Now, to discuss in transit. In most cases, a website should have SSL and you can see that by looking at the URL bar:
It should be green and the lock should be closed. Similarly, file transfers should be over SSH, HTTPS or SFTP, look for the “S”! This simply protects against the transit portion of this, but be mindful of websites and make sure you have proper URLs and that you trust the source of the site. Don’t click on links that you aren’t expecting or don’t trust and be fooled by relying on the green lock. Just because the connection is using encrypted communication, does not mean that the website is legitimate. If the site warns you by saying it might not be safe, don’t click “Proceed” or “Continue anyway” without considering the implications.
Password Management
Encryption means nothing without having a password set, make sure you set up a pin, fingerprint, or password on your mobile devices! Proper password management is also necessary as credentials are constantly getting stolen or people end up with a pattern for how they personally choose passwords. Having a tool to manage unique passwords for each account helps reduce the amount of accounts affected in the case of a compromise, whether phishing or otherwise.
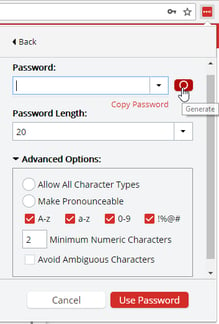
I use a combination of password management tools. Locally, Password Safe (Windows) and then in my browser, LastPass. You can install this as a browser extension, fairly easily.
Use these tools to generate long, random, meeting the criteria, passwords that you don’t have to remember.
You simply have to remember one password, a master password to get into your vault. That being said, you can’t rely on one password alone to unlock all of your data, you also need Multi-Factor Authentication.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Even if you have a great password, if you’re accessing something on the Internet, it’s just a matter of time before your credentials are stolen or someone cracks your password to get in. Having Multi-Factor Authentication requires more than one factor to gain access. The factors of the multi-factor authentication mechanism fall into three categories: knowledge (something you know), possession (something you have), and inherent (something you are). You may have something available at work that utilizes this, VPN, certain jump boxes, etc.
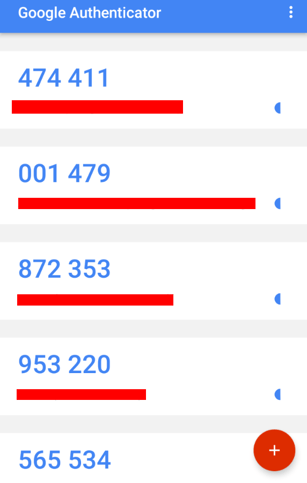
At home, you should set up all Internet-facing accounts with multi-factor authentication. This would include your email, your new LastPass account, github and your bank accounts! For most implementations of infrastructure, you can use Duo Security or Google Authenticator which will give you a rotating token to type in after you’ve typed in your username and password pair, this is the preferred method.
Some banks only allow texting a number to your cell phone that you have to type in. Make sure you have this turned on and if you do, also make sure that the text isn’t able to be viewed from your phone’s locked screen! If your bank doesn’t even support that, it’s time to find a new bank.
These three technical controls will help you in the majority of cases that people fall victim to. Whether your laptop is stolen, whether you’re accessing information on the Internet or your credentials get compromised due to phishing, these will slow down hackers and force them to find a new target.